Bacterial Spread
When the tooth pulp becomes necrotic secondary to severe caries, infection can spread to become a potentially life-threatening cellulitis.
Untreated oral bacterial infection can cause:
- Intraoral abscesses
- Sinusitis
- Facial and periorbital cellulitis
- Brain abscesses
- Bacteremia and sepsis
- Airway compromise secondary to infection tracking into fascial planes of the neck
Sinusitis, bacteremia, and brain abscess may occur due to direct bacterial extension into adjacent soft tissues, or systemically through the hematogenous route.
Aspiration Pneumonia
- Aspiration of oral bacteria is associated with pneumonia, particularly in bedridden and hospitalized patients.
- Eighty-three percent of patients who develop nosocomial pneumonias are mechanically ventilated.
- Oral care interventions led to a 90% reduction in ventilator associated pneumonia in adult ICUs.
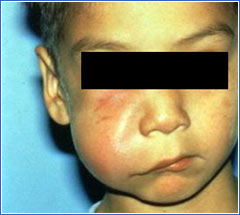
Child with right facial swelling due to cellulitis originating from a necrotic tooth
References
Hutchins K, Carras G, Erwin J, et al. Ventilator- associated pneumonia and oral care: A successful quality improvement project. Am J Infect Control. 2009; 37:590-7.
Ehrenzeller S, Klompas M. Association Between Daily Toothbrushing and Hospital-Acquired Pneumonia: A Systematic Review and Meta-Analysis. JAMA Intern Med. 2024;184(2):131–142. doi:10.1001/jamainternmed.2023.6638