Oral Piercings and Grills
Piercings
The American Academy of Pediatric Dentistry (AAPD) "strongly opposes" the practice of piercing perioral and intraoral tissues and use of jewelry on these tissues.
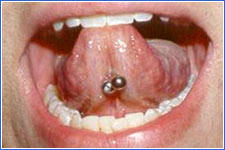
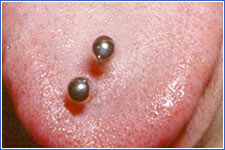
Oral piercings are increasingly popular, but there are significant risks.
Procedure-related risks:
- Swelling – most common symptom post-piercing
- Prolonged bleeding
- Nerve damage
Jewelry-Related Complications:
- Injury to the gums and dental fractures, scarring
- Interference with oral hygiene, speech, chewing and swallowing
- Allergic/hypersensitivity reaction to metal
- Aspiration or ingestion if jewelry becomes loose
For treatment information, see "Oral piercing complications" page
in the Acute Dental Problems module".
Grills
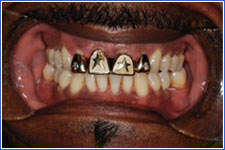
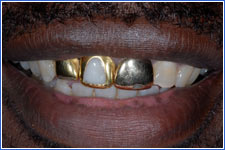
Grills on the teeth can increase the risk of developing caries and trigger allergic reactions to the metal.
- Counsel grill-wearers to:
- Remove the grill to eat and sleep
- Brush and floss regularly
- Limit amount of time the grill is worn
References
Policy on Intraoral/Perioral Piercing and Oral Jewelry/Accessories. Pediatr Dent. 2018 15; 40(6):84-85.