Alveolar Bone Fracture
Jaw fractures typically present in the emergency room, usually in conjunction with other facial injuries associated with blunt trauma. Current imaging recommendations lean toward facial and head CT, as plain films often miss facial fractures. MRI has proven benefits in assessing traumatic soft tissue injuries.
Symptoms & Findings
- Localized tenderness
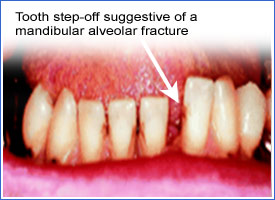
- Step-offs in occlusion of the teeth and alveolar bone on palpation represent alveolar bone fractures. Visible displacement may not be present even with fracture
- Movement of segmental alveolar fractures when assessing tooth mobility
- Gingival laceration
Referral
- See dentist or oral surgeon emergently
- Reduction is easier before swelling occurs
References
A.B. van As, A.J. van Loghem, B.F.J. Biermans, T.S. Douglas, N. Wieselthaler and S. Naidoo, Causes and distribution of facial fractures in a group of South African children and the value of computed tomography in their assessment, International Journal of Oral and Maxillofacial Surgery. 2006. 35(10):903-906.
International Association of Dental Traumatology. Dental Trauma Guidelines, Revised 2020. https://www.iadt-dentaltrauma.org/for-professionals.html.
American Academy of Pediatric Dentistry. Guideline on Management of Acute Dental Trauma. Pediatric Dentistry. 2009; 31(6):187-195.