Characteristics of Primary Teeth and Injury Types
The alveolar bone is more pliable in children than adults, making intrusion and luxation injuries of primary teeth more common. As permanent teeth develop in close proximity to primary teeth, intrusion or subluxation of primary teeth present a risk for damage the developing underlying permanent tooth.
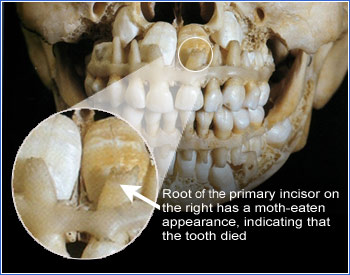
In the child's skull pictured on the right, the tip of the root of the right primary incisor has a moth-eaten appearance, indicating that the tooth died. Since no decay is evident, this was probably caused by an injury - most likely intrusion as the tooth appears shorter than the adjacent teeth.
The primary tooth death resulted in chronic infection that damaged the entire facial surface of developing enamel of the underlying permanent tooth, causing hypoplasia (brown discoloration) of the enamel.
References
McTigue DJ. Diagnosis and management of dental injuries in children. Pediatric Clinics of North America. 2000;47(5):1067-84.
American Academy of Pediatric Dentistry. Guideline on Management of Acute Dental Trauma. Pediatric Dentistry 2009;31(6):187-195.
Scheid RC, Weiss G. Woelfel's Dental anatomy, Enhanced Edition. 9th ed. Wolters Kluwer; 2020.