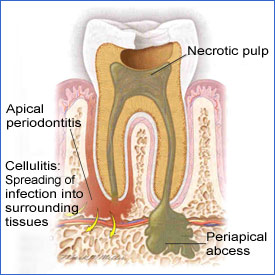
Periapical Abscess
A periapical abscess is a localized, purulent form of periapical periodontitis.
The abscess can track through the bone to the soft tissue creating a localized fluctuant swelling, normally adjacent to the affected tooth root. The abscess will then fistulize and drain or spread to surrounding tissues causing cellulitis.
Symptoms
- Pain is well localized.
- Tooth is typically percussion sensitive.
- Pain may be severe, spontaneous, and persistent.
- If the abscess is draining, pain may be less severe.
Treatment & Referral
- Arrange urgent dental referral for root canal or extraction.
-
- If tooth is not definitively treated, abscess is likely to recur.
- Incision and drainage can provide temporary relief if not naturally draining.
- Analgesics are necessary.
- Antibiotics required only if concurrent cellulitis is present.
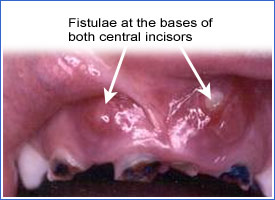
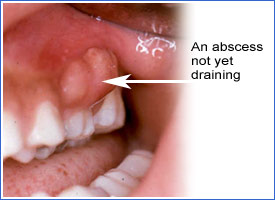
Clinical Examples
References
Sutherland S, Matthews DC. Emergency management of acute apical periodontitis in the permanent dentition: a systematic review of the literature. Journal Canadian Dental Association. 2003;69(3):160.
Karamifar K, Tondari A, Saghiri MA. Endodontic Periapical Lesion: An overview on the etiology, diagnosis, and current treatment modalities. European Endodontic Journal. 2020;5(2):54.