Leukoplakia and Erythroplakia
Oral leukoplakia, the best-known premalignant oral lesion, is defined as "a white patch or plaque that cannot be characterized clinically or pathologically as any other disease." Analogous red lesions are called erythroplakia, and combined red and white lesions are also known as speckled leukoplakia or erythroleukoplakia.
Symptoms
- Leukoplakia and erythroplakia are often subtle and asymptomatic.
- Lesions begin as a white or red patch.
- Progression may lead to slightly elevated plaques.
- Lesions with ulceration are more likely to be cancerous.
- Erythroplakia and speckled leukoplakia are more likely to exhibit dysplasia or carcinoma upon microscopic examination.
Treatment
- All unexplained white lesions in the mouth should be referred to a dentist, oral surgeon, or ENT for evaluation and biopsy.
- Leukoplakia or erythroplakia exhibiting moderate or severe dysplasia should be surgically removed if possible.
- Cryotherapy and laser ablation have been used, although these methods do not allow for tissue preservation and microscopic examination.
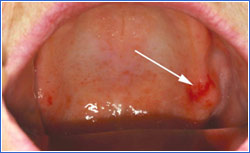
Red Erythroplakia
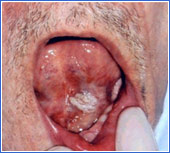
White Leukoplakia
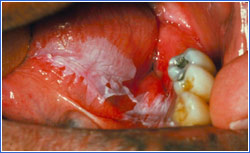
Red/White Leukoplakia
References
Truman BI, Gooch BF, Sulemana I, Gift HC, Horowitz AM, Evans CA, et al. Reviews of evidence on interventions to prevent dental caries, oral and pharyngeal cancers, and sports-related craniofacial injuries. Am J Prev Med 2002;23:21-54.
Neville BW, Day TA. Oral cancer and precancerous lesions. Ca: a Cancer Journal for Clinicians. 2002;52(4):195-215.
Lodi G, Sardella A. Bez C, et al. Interventions for treating oral leukoplakia. Cochrane Database of Systematic Review. 2006; 18(4): CD001829.
Speight PM, Khurram SA, Kujan O. Oral potentially malignant disorders: risk of progression to malignancy. Oral Surg Oral Med Oral Pathol Oral Radiol. 2018; 125(6): 612-627.