Periodontitis
Periodontitis is deep inflammation of the periodontium which occurs in response to bacterial plaque on teeth. Progression of the disease results in destruction of the supporting bone, increasing tooth mobility and eventually causes tooth loss. It is a relatively common oral disease affecting 15% of pregnant women.
Symptoms
- Periodontitis in its earliest stages may have no obvious symptoms.
- Dentists can detect early disease through clinical probing of the gingiva and radiographs.
- Patients with advanced disease have loose teeth.
Etiology
- Chronic exposure of the periodontal tissues to bacterial plaque cause a chronic inflammation.
- Progression of the disease is partly determined by body's host response to the bacteria, either magnifying or suppressing the inflammatory response.
- Chronic inflammation leads to destruction of the periodontal ligament, loss of supporting bone, tooth loosening, and eventual tooth loss.
- Smoking, diabetes, HIV, pregnancy, and poor oral hygiene can all contribute to the development of periodontitis.
Preventive Measures & Treatment
- Good oral hygiene and regular dental visits to monitor hygiene and remove subgingival plaque helps to prevent or control inflammation.
- Established disease may require more advanced dental treatment including deep root scaling (cleaning below the gum surface) and antibiotics.
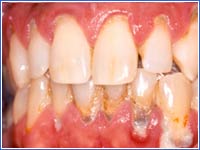
Moderately Severe Periodontal Disease
References
Boggess KA. Maternal Oral Health in Pregnancy. Obstet and Gynecol. 2008; 111(4):976-986.
Novak MJ. Classification of diseases and conditions affecting the periodontium. In: Clinical Periodontology. M.G. Newman, H. H Takei, F. A. Carranza Eds. Philadelphia: W.B. Saunders, 2002.